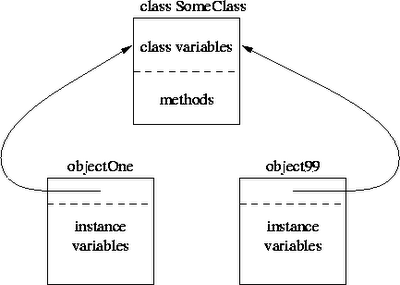
- Variables that are common to all objects.
- Fields that have the static modifier in their declaration are called static fields or class variables. They are associated with the class, rather than with any object.
- Every instance of the class shares a class variable, which is in one fixed location in memory.
- Any object can change the value of a class variable.
- class variables can also be manipulated without creating an instance of the class.
- e.g: If you are going to create a variable serial number for an Item, which is unique for each, you can consider to declare a variable as static because no matter how many instance of class you create, they are also sharing the static variable.
Author: dicksonkho
Java Variable Naming Convention
- The first letter of a class name should be capitalized.
- The first (or only) word in a method name should be a verb.
- By convention, method names should be a verb in lowercase or a multi-word name that begins with a verb in lowercase, followed by adjectives, nouns, etc. In multi-word names, the first letter of each of the second and following words should bezed. Eg: getFinalData
Click HERE for more..
How to – Struts
1. Create struts-config.xml
(To store the configuration within project)
2. Create WelcomeInput.jsp
(Create User input file)
3. Create ContactFormBean.java
(Get and Set those variable pass from jsp page)
4 Create SignupAction.java
(Java class which use to manipulate the data/variable)
5. Create confirmation.jsp
(Display result of manipulated data)
For example: Click Here (netBeans Projects)
For brief concept, Click Here
How to – log4j
1. Have log4j jar file to place into:
 2. Have property file to place into :
2. Have property file to place into :

3 .Example property file will :
log4j.rootLogger=WARN, Other log4j.appender.Other=org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender log4j.appender.Other.File=D:/Work/web/WEB-INF/logs/root.log log4j.appender.Other.MaxFileSize=1000KB log4j.appender.Other.MaxBackupIndex=3 log4j.appender.Other.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.Other.layout.ConversionPattern=%d [%t] %-5p %c - %m%n log4j.logger.my.com.leadingside=DEBUG, appLog log4j.additivity.my.com.leadingside=false log4j.appender.appLog=org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender log4j.appender.appLog.File=D:/Work/web/WEB-INF/logs/app.log log4j.appender.appLog.MaxFileSize=1000KB log4j.appender.appLog.MaxBackupIndex=3 log4j.appender.appLog.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.appLog.layout.ConversionPattern=%d %-5p %c - %m%n
4. Copy below code for testing
import org.apache.log4j.Level;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
public class TestLogger{
static Logger myLogger = Logger.getLogger(TestLogger.class.getName( ));
public static void main(String [] args){
myLogger.setLevel(Level.DEBUG);
myLogger.warn("SUccess Debug From LOGER");
}
}
5. NOTE / Attention !!
DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR, FATAL
following sequense, debug is the lowest level, means, it will log for
INFO, WARN, ERROR, FATAL
BUT if we set level to WARN, logger will log only ERROR, FATAL.
eg: myLogger.setLevel(Level.ERROR);
myLogger.warn(“SUccess Debug From LOGER”);